Home » Professional »
THE BIOLOGY OF WOUND HEALING
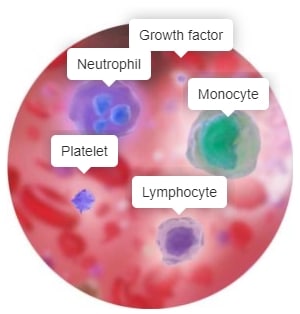
The important components of blood reaching a wound are; immune cells, platelets and growth factors. These components help orchestrate the wound healing response.32
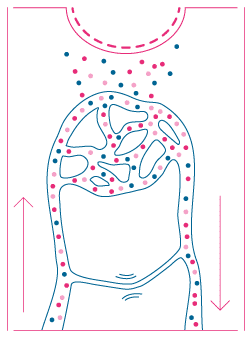
Wound healing demands an increased blood supply via the microvascular system.36 This is accomplished primarily by the contraction of arteriovenous shunts (AV) that direct the blood to the wound area.37, 38
WATCH OUR 3D-ANIMATION
AV SHUNTING
AV shunting is followed by vasodilation and the extravasation of immune cells, primarily neutrophils, monocytes that become macrophages in the tissue, and lymphocytes, into the wound. These cells are important for clearing pathogens and debris, but they also orchestrate healing.36
The shift from a non-healing but pathogen-clearing macrophage phenotype (M1) to a healing one (M2) is crucial for the transition into the reparative wound healing phase.39, 40
NON-FUNCTIONAL AV SHUNTING
In chronic wounds, such as hard-to-heal diabetic foot ulcers, the capillary blood circulation is often reduced, leading to chronic capillary ischemia.
The denervated arteriovenous (AV) shunts lose their normal contraction response and stay open, leading to blood by-passing the capillaries and preventing important blood components, needed to orchestrate wound healing, from reaching the wound site.
In diabetic patients, it is the continuous excess blood glucose that results in chronic capillary ischemia due to neuropathy. The neuropathy causes non-functional shunting and impaired microvascular flow.41
These microcirculatory vasomotor changes correlate with the severity of peripheral neuropathy in patients with type-2 diabetes. The consequence is reduced vasodilation and reduced leukocyte infiltration of the wound area.42
IN NEUROPATHIC PATIENTS NO SHUNTING IS SEEN
AV SHUNTING
AV shunting is part of the normal healing response. Immune cells, platelets and growth factors reach the wound.
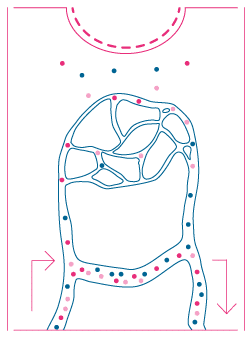
NON-FUNCTIONAL AV SHUNTING
In neuropathic patients no shunting is seen, leading to a poor healing response.
